Page 14 - Demo
P. 14
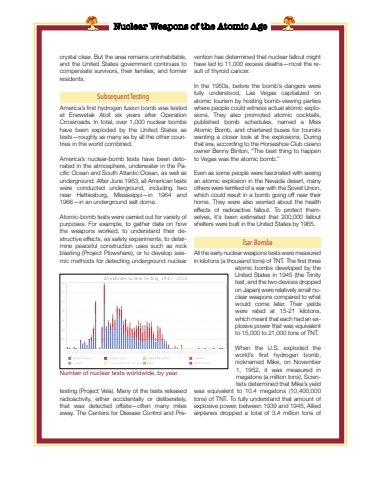
Nuclear Weapons of the Atomic Agecrystal clear. But the area remains uninhabitable, and the United States government continues to compensate survivors, their families, and former residents.Subsequent TestingAmerica%u2019s first hydrogen fusion bomb was tested at Enewetak Atoll six years after Operation Crossroads. In total, over 1,000 nuclear bombs have been exploded by the United States as tests%u2014roughly as many as by all the other countries in the world combined.America%u2019s nuclear-bomb tests have been detonated in the atmosphere, underwater in the Pacific Ocean and South Atlantic Ocean, as well as underground. After June 1963, all American tests were conducted underground, including two near Hattiesburg, Mississippi%u2014in 1964 and 1966%u2014in an underground salt dome. Atomic-bomb tests were carried out for variety of purposes. For example, to gather data on how the weapons worked, to understand their destructive effects, as safety experiments, to determine peaceful construction uses such as rock blasting (Project Plowshare), or to develop seismic methods for detecting underground nuclear testing (Project Vela). Many of the tests released radioactivity, either accidentally or deliberately, that was detected offsite%u2014often many miles away. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has determined that nuclear fallout might have led to 11,000 excess deaths%u2014most the result of thyroid cancer.In the 1950s, before the bomb%u2019s dangers were fully understood, Las Vegas capitalized on atomic tourism by hosting bomb-viewing parties where people could witness actual atomic explosions. They also promoted atomic cocktails, published bomb schedules, named a Miss Atomic Bomb, and chartered buses for tourists wanting a closer look at the explosions. During that era, according to the Horseshoe Club casino owner Benny Binton, %u201cThe best thing to happen to Vegas was the atomic bomb.%u201d Even as some people were fascinated with seeing an atomic explosion in the Nevada desert, many others were terrified of a war with the Soviet Union, which could result in a bomb going off near their home. They were also worried about the health effects of radioactive fallout. To protect themselves, it's been estimated that 200,000 fallout shelters were built in the United States by 1965. Tsar BombaAll the early nuclear weapons tests were measured in kilotons (a thousand tons) of TNT. The first three atomic bombs developed by the United States in 1945 (the Trinity test, and the two devices dropped on Japan) were relatively small nuclear weapons compared to what would come later. Their yields were rated at 15-21 kilotons, which meant that each had an explosive power that was equivalent to 15,000 to 21,000 tons of TNT. When the U.S. exploded the world%u2019s first hydrogen bomb, nicknamed Mike, on November 1, 1952, it was measured in megatons (a million tons). Scientists determined that Mike%u2019s yield was equivalent to 10.4 megatons (10,400,000 tons) of TNT. To fully understand that amount of explosive power, between 1939 and 1945, Allied airplanes dropped a total of 3.4 million tons of Number of nuclear tests worldwide, by year.